History: A 75-year-old man with a chronic history of microhematuria was referred for a CT urogram by his urologist.
病史:75岁男性,长期镜下血尿,泌尿外科医生建议其行CTU检查。
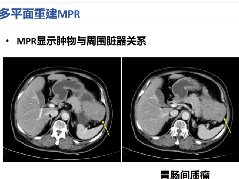
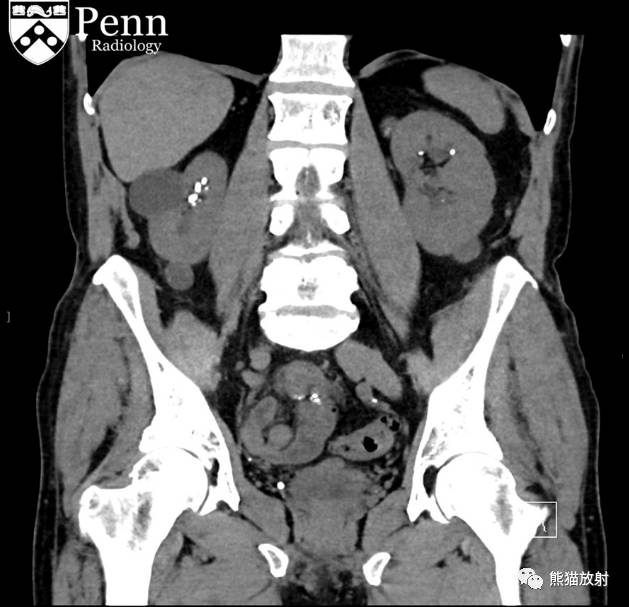
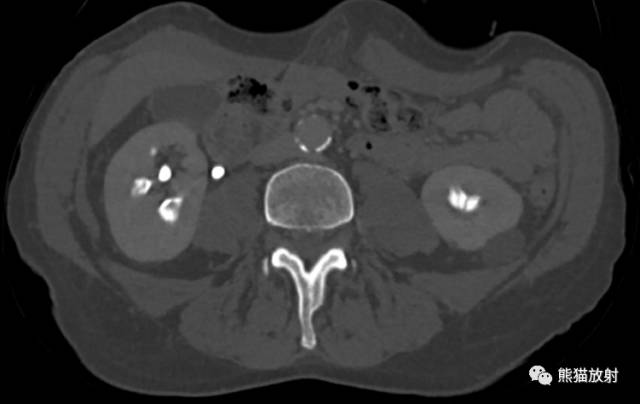
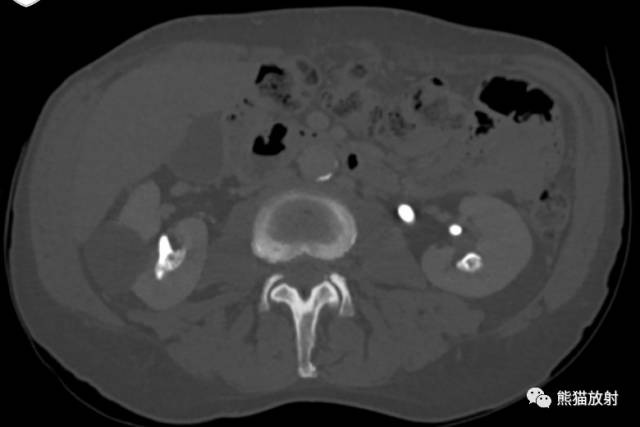
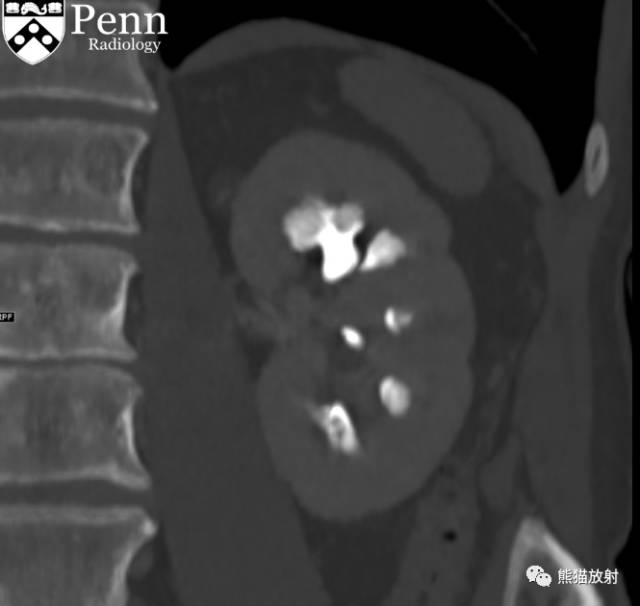
Scout, coronal precontrast, axial nephrographic/excretory phase images, and volume-rendered coronal reconstructions of the left and right kidneys are shown below.
定位像、冠状平扫、轴位排泄期图像及左、右肾冠状VR重建如下所示。
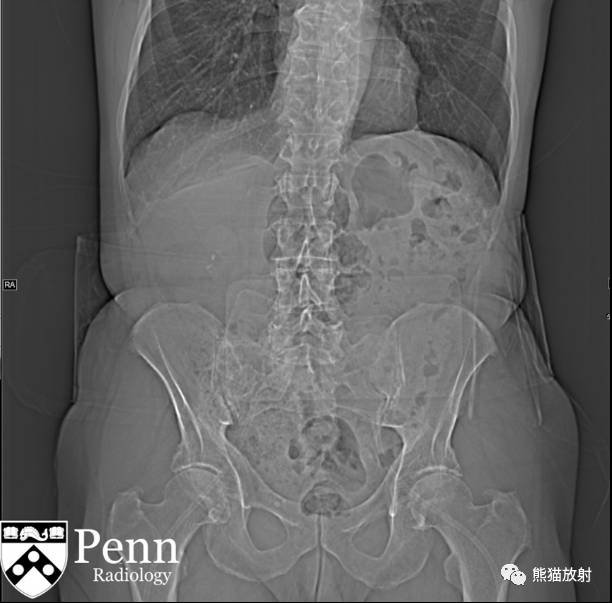
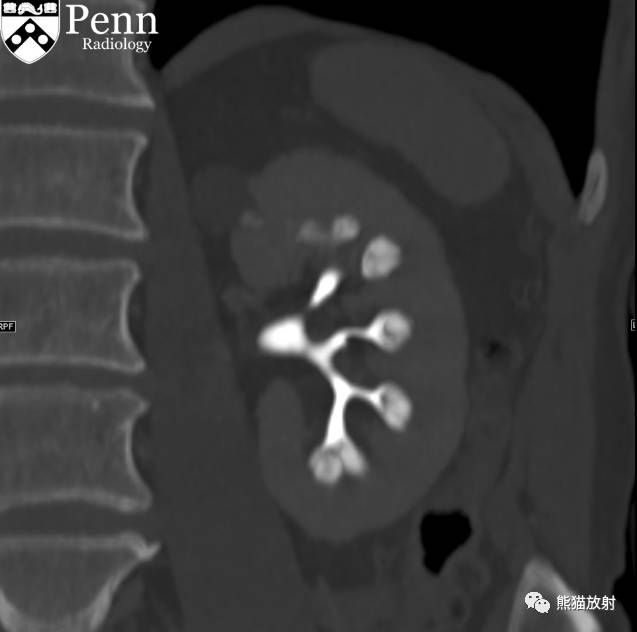
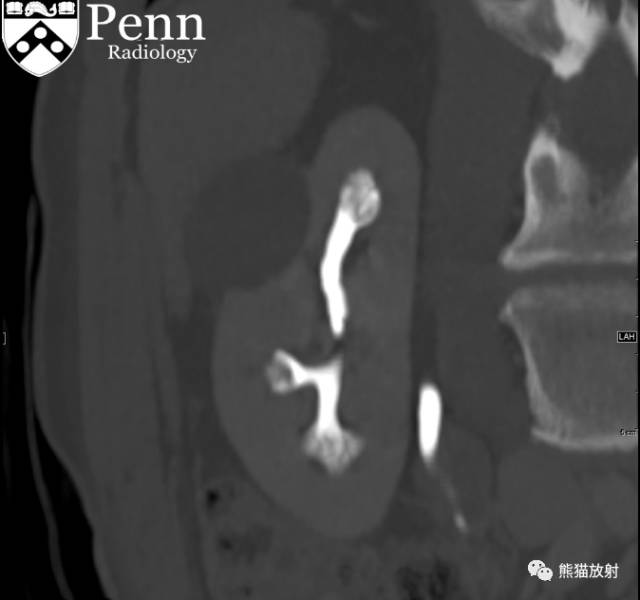
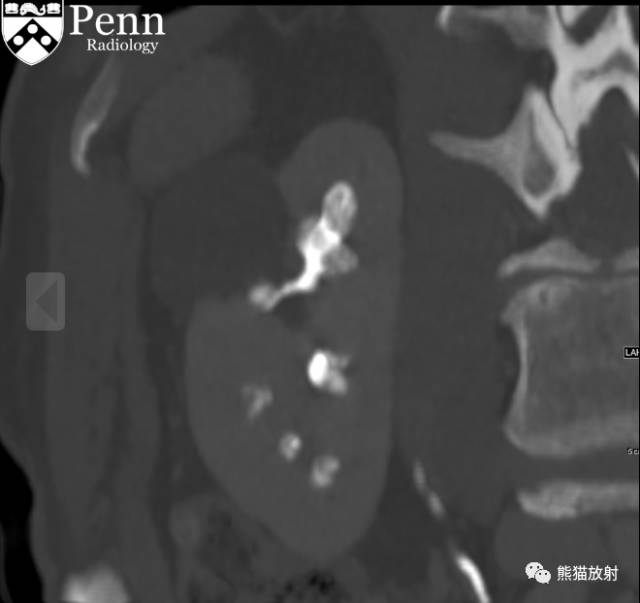
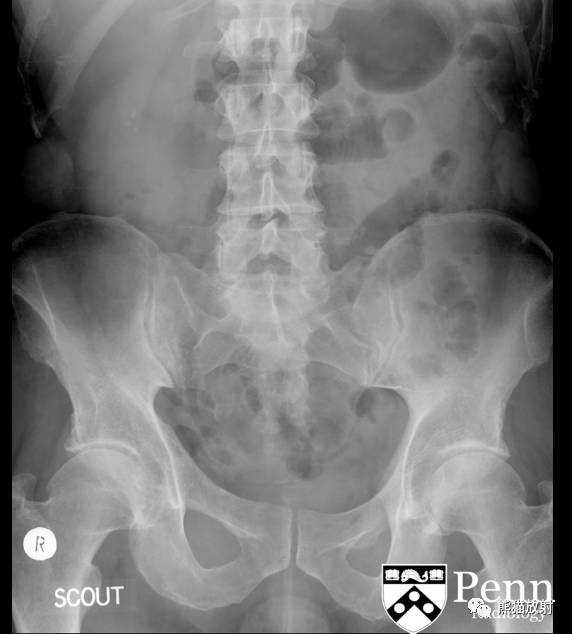
Additional history: The patient has a prior history of microhematuria and kidney stones. Review of the PACS for prior imaging reveals an intravenous pyelogram (IVP) from 2005. Scout and postcontrast exposures are shown below.
病史补充:患者之前患有镜下血尿及肾结石。回顾PACS中2005年的静脉尿路造影(IVP)图像,腹部平片及造影后图像图像所示。
Findings 影像表现
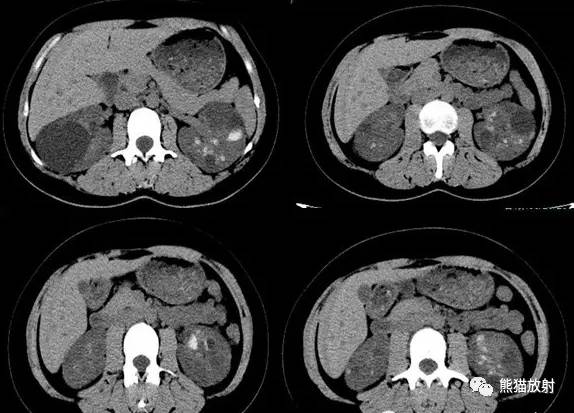
CT urogram (2017): Noncontrast images demonstrate multiple bilateral nonobstructing renal calculi, the largest measuring 6 mm in the right kidney. Some of the calcifications could represent nephrocalcinosis — for example, those in the upper pole of the right kidney. The kidneys show symmetric enhancement without suspicious renal mass. Multiple bilateral exophytic simple renal cysts are noted, the largest in the midpole of the right kidney measuring 3.6 x 4.3 cm. There are additional subcentimeter low-attenuation lesions that are too small to characterize. There is a “paintbrush sign” appearance to the renal medullae in keeping with a history of medullary sponge kidney. There is mild bladder wall thickening and trabeculation that may be related to chronic outlet obstruction. Further evaluation is deferred to cystoscopy.
CTU:CT平扫可见双肾多发非梗阻性肾结石,右肾最大者直径约6mm,其中一些钙化可能代表肾结石,例如,右肾上极的那些。肾脏对称性强化,未见可疑肾肿物。双肾可见多发单纯性肾囊肿,大者位于右肾中部,大小约3.6 x 4.3 cm;另可见不足1cm的低密度灶,其太小而不能显示。肾髓质表现为“毛刷征”,符合髓质海绵肾。膀胱壁轻度增厚并小梁形成,与慢性流出道梗阻有关。进一步评估需膀胱镜检查。
IVP (2005): Preliminary scout images demonstrate a cluster of at least three radiopaque stones in the upper pole of the right kidney; the largest two stones in this cluster each measure 6 mm in diameter. In addition, there are probable clusters of smaller stones in the interpolar right kidney and right lower pole. Following the uneventful intravenous administration of 150 mL of nonionic contrast material, prompt nephrograms develop, which show the kidneys to be normal in size, shape, appearance, and internal architecture. There is diffuse bilateral tubular ectasia. Contrast is excreted promptly into otherwise normal-appearing pyelocalyceal systems. The calculi are no longer seen and likey reside in dilated tubules. The ureters are normal in course, caliber, and appearance. The urinary bladder has a mildly trabeculated appearance. There are two small urinary bladder diverticula: one of the bladder dome and one arising from the left lateral bladder wall. No filling defects are seen.
IVP:预扫定位像可见右肾上极至少3个阳性结石,簇状分布,最大的两个直径约6mm。另右肾中部及下极可见成簇的小结石。静脉注射非离子型对比剂150ml,立即摄片,可见肾脏大小、形态、表现及内部结构正常,可见弥漫性双侧肾小管扩张,造影剂进入正常的肾盂肾盏系统。钙化并未显示,可能在扩张的肾小管内。输尿管走行、直径及表现正常,膀胱轻度小梁形成,可见两个小膀胱憩室,一个位于膀胱顶壁,一个位于左侧壁;未见充盈缺损。
Differential diagnosis
鉴别诊断:
Diagnosis: Medullary sponge kidney
最后诊断:髓质海绵肾
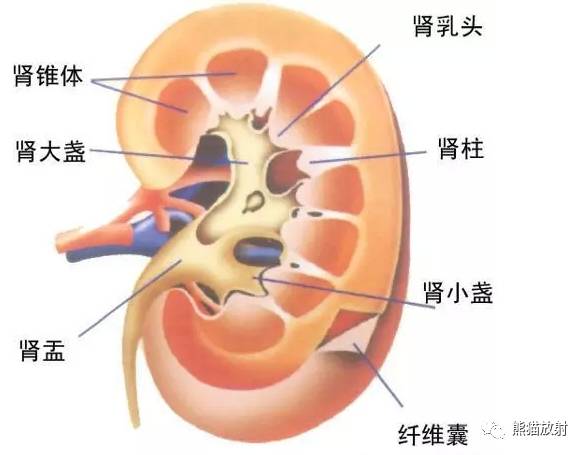
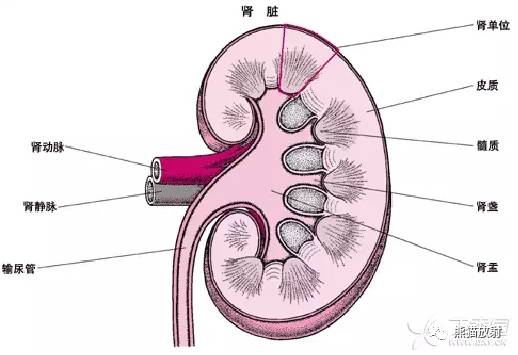
Medullary sponge kidney (MSK)
Pathophysiology
病理生理
髓质海绵肾(MSK)多散发,是指肾髓质及肾乳头部分的集合管发育不良并扩张,大部分情况下,可合并髓质肾结石。偶尔具有遗传性。
患者可表现为尿路瘀滞并导致肾结石;
多达33%-50%的患者有高血钙症(也就是,甲旁亢表现);
病因及发病机制不明;
横切面上,肾脏表现为海绵样,在肾锥体可见多发小囊腔。囊内包含黄棕色液体及脱落细胞或钙化物质;囊内结石,囊壁包含草酸钙有或无磷酸钙。
肾结石的大小及数目随时间逐步增加;
可双侧(75%) 或单侧(25%),可累计单个或部分肾锥体;
MSK的预后通常较好,患者寿命正常,除非有并发症,包括感染,大量结石形成,肾功能不全、肾衰。
Epidemiology
流行病学
女性多见;发病率约在5000-20000分之一;
0.5%在尿路造影时偶然发现; 2%-21%在肾结石患者检查时偶然发现。
Clinical presentation
临床表现:
大部分患者无症状,因其它原因行尿路检查时偶然发现;
然而,约10%的患者因并发尿路感染、血尿、肾结石而表现出相关症状。
Imaging features 影像表现
Radiography: May see medullary nephrocalcinosis (calcifications within medulla) or urolithiasis.
平片:可见肾髓质钙质沉着(髓质内钙化)或尿路结石
IVP:
IVP:
Retrograde pyelography:
逆行尿路造影:
CT:
CT:
MRI:
MRI:
Treatment
There is no treatment for medullary sponge kidney. Treatment is based on managing complications when they arise, such as the following:
治疗:MSK无需治疗,治疗主要是针对相关并发症,例如:
男,41岁,临床发现双肾结石10年。
女性患者,24岁,体检发现。

鉴别诊断:
1)肾结石:位于肾盂或肾小盏内,增强后排泌的造影剂常把结石掩盖,较大的结石常使其以远的肾盏发生梗阻性积水。
2)肾结核:一般常单侧发生,肾实质内可见单发或多发大小不等、形态不一的囊腔,囊壁有钙化斑,局部肾盏可见不规则的破坏或造影剂充盈不佳,常并发有肾盏、肾盂积水。
3)肾乳头坏死:愈合期表现为集合小管内或周围弥散性钙盐沉积,钙化较海绵肾更广泛。
 纵隔大细胞神经内分泌癌1例CT影像
纵隔大细胞神经内分泌癌1例CT影像  张力性纵隔气肿影像表现及严重度分级
张力性纵隔气肿影像表现及严重度分级  迅速增大的肺部结节,首先考虑良性,确诊需要肺穿
迅速增大的肺部结节,首先考虑良性,确诊需要肺穿  肺隔离症:易误诊为肺癌的占位性病变,肺穿刺禁忌!
肺隔离症:易误诊为肺癌的占位性病变,肺穿刺禁忌!  肺段与肺内管道应用解剖
肺段与肺内管道应用解剖  肺转移瘤的十种不典型CT表现
肺转移瘤的十种不典型CT表现  肺内淋巴结的CT表现特点及与病理对照
肺内淋巴结的CT表现特点及与病理对照  肺实变与肺不张的CT鉴别诊断
肺实变与肺不张的CT鉴别诊断  医生现身说法,这五种忙帮不得!
医生现身说法,这五种忙帮不得!  北大教授:要真正让医务人员有阳光体面的收入!医
北大教授:要真正让医务人员有阳光体面的收入!医  为值夜班的医生护士鼓与呼:请给我们更多关注!
为值夜班的医生护士鼓与呼:请给我们更多关注!  广东拟取消医院用药数量限制,满足患者多样性需求
广东拟取消医院用药数量限制,满足患者多样性需求  博士、硕士入职就给精装房!又有医院不惜下血本招
博士、硕士入职就给精装房!又有医院不惜下血本招  历时7年之久,温医生宣判无罪!
历时7年之久,温医生宣判无罪!  重磅!四川发文:严禁限制医生多点执业
重磅!四川发文:严禁限制医生多点执业  与真人医生诊断一致性达96%:AI医生应用前景广阔
与真人医生诊断一致性达96%:AI医生应用前景广阔